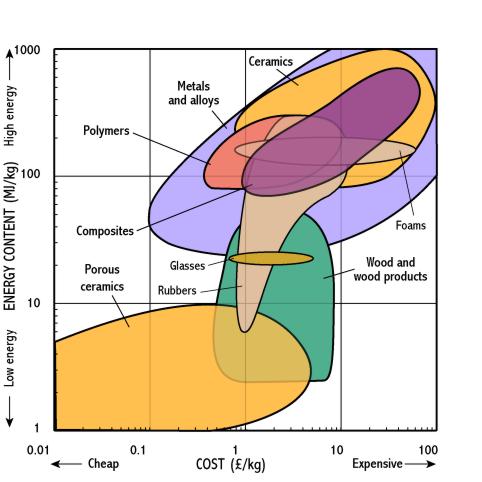
Energy - Cost
Class level
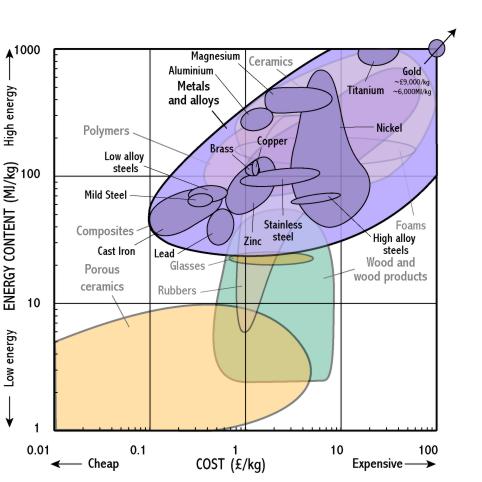
Metals and alloys
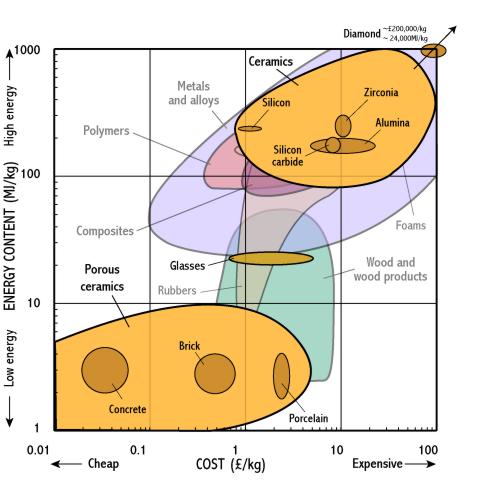
Ceramics
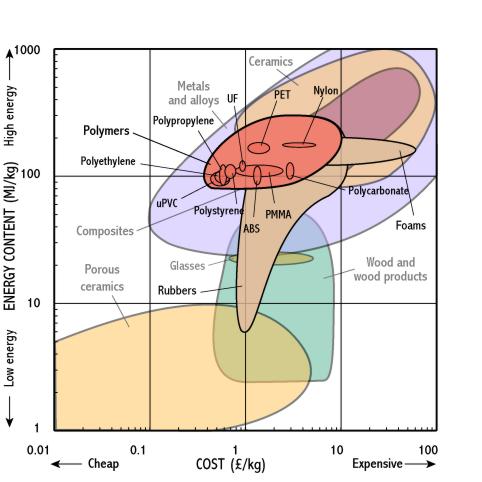
Polymers
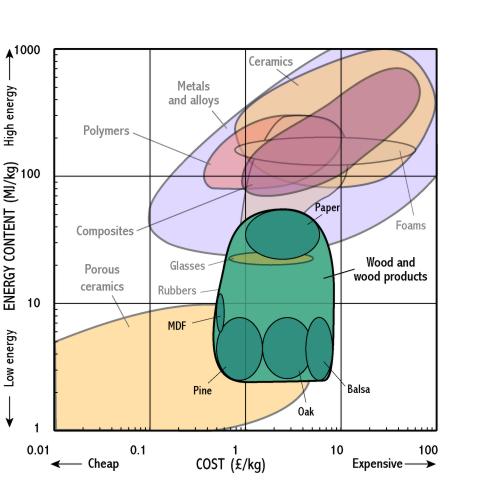
Wood and wood products
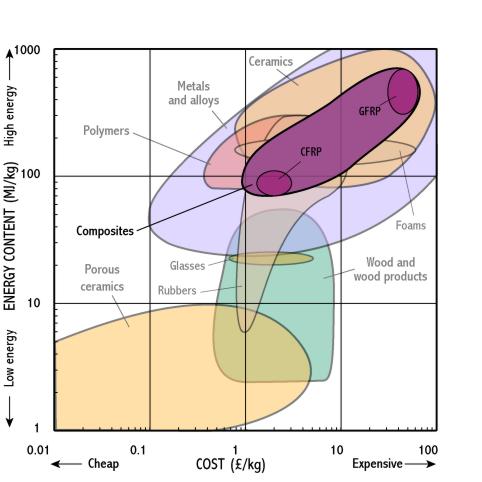
Composites
General Information
- In general the energy required to produce a material is a large factor in the raw material cost. As a result most materials lie on a line from bottom left (low cost/low energy content) to top right (high cost/large energy content).
- It is difficult to assess the environmental impact of using one material over another since there are many factors from production to disposal.
- The energy content used to produce a material gives a rough indication of the environmental cost of production
- For materials which are energy intensive to produce there are large cost and energy savings by recycling e.g. aluminium cans
- Gold is a precious metal which can be sold for a very high price; this means that more energy can be spent in extracting it by mining rocks containing only a small fraction of gold
Physical Insights
- Measuring the energy content of a material is difficult, but includes:
- the energy required to collect/mine the material
- the energy required to refine, extract or synthesise it
- Polymers are made by refining and processing hydrocarbons from oil - the energy used per kilogram is similar to the energy needed to produce many metals
- Construction materials such as concrete, brick and woods require relatively little energy to produce them and are thus cheap
- Metals are usually extracted from their oxide - this takes up a lot of energy, for example, one twentieth of the total energy consumption in the United States is used to produce aluminium
Example Uses
- To select materials which have less environmental impact and contribute less to global warming
- To consider environmental impact for one-use disposable products - e.g. disposable gowns, sheeting etc in hospitals are made from paper
- To consider environmental impact for high volume, energy-intensive products such as cars
Simple Questions
- Why is it economic to recycle aluminium cans but less so for steel ones?
- Why will new reserves of minerals/oil which are not now economic to mine become economic in the future?
- Select materials for a wall/fence around your house.
- Select materials for fast-food restaurant eat-in plates, trays, etc
- Select materials for bedding for cattle.
Further Questions
- Why doesn’t energy produced by wind-turbines lead to global warming?
- Why is the controlled burning of polymers an environmental option to landfill?
- Give one application where diamonds are used in industry and explain why.
There are 2 separate populations for this class to improve clarity. Move the mouse over different parts of the class name to reveal each one.
Select chart:





