Go to the basic non-Java version. Return to the charts main page
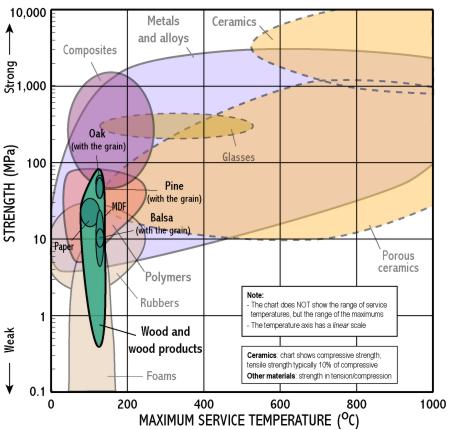
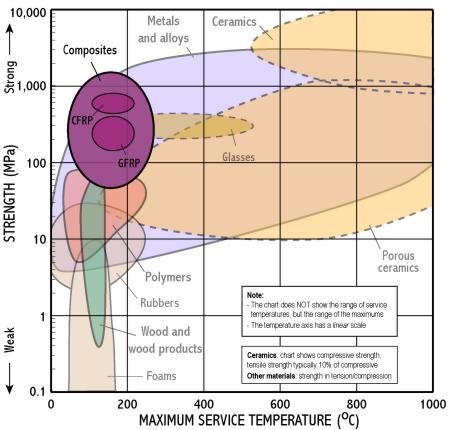
Strength - Max. service temperature
Rollover class name to view individual materals, click chart to return to class view. Hover mouse over property for brief definition.
![]()


General Information
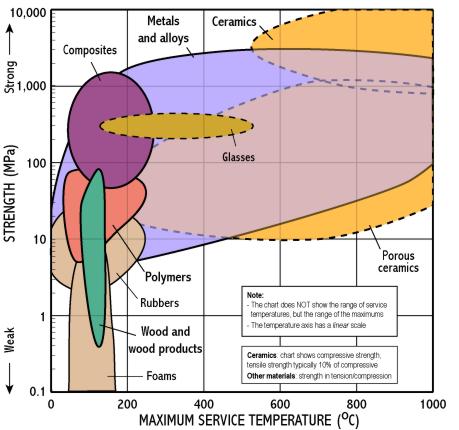
- Strength measures the resistance of a material to failure, given by the applied stress (or load per unit area)
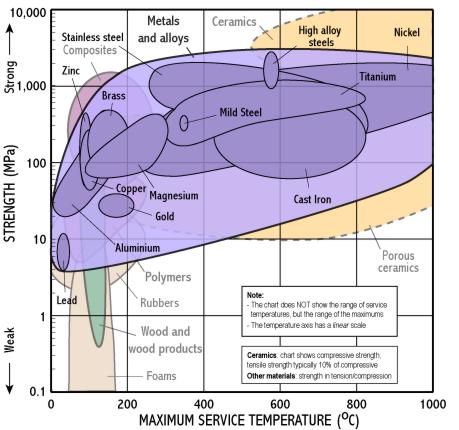
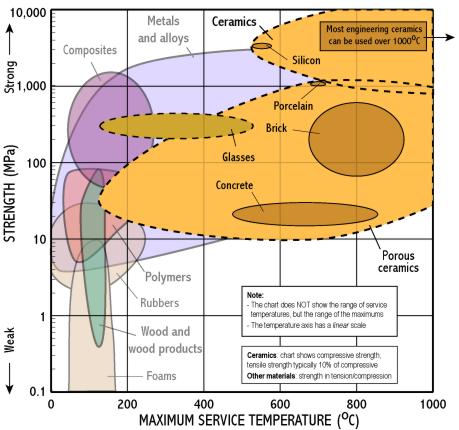
- The chart shows yield strength in tension for all materials, except for ceramics for which compressive strength is shown (their tensile strength being much lower)
- Maximum service temperature indicates the maximum temperature at which a material can be used in engineering – above this its strength rapidly decreases
- This chart is useful for identifying materials for components which operate at temperatures above room temperature, e.g. cooking utensils, car engines and exhausts
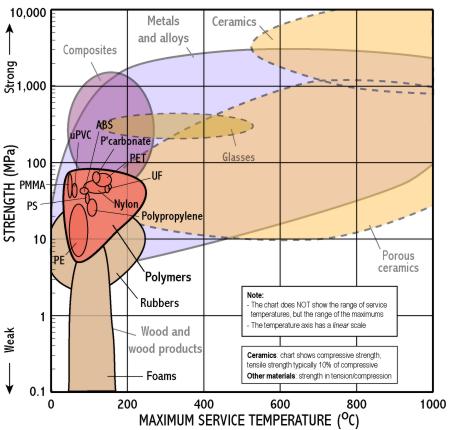
- Polymers are limited to low temperatures, metals to intermediate temperatures, and only ceramics can withstand very high temperatures.
Physical Insights
- Thermoplastic polymers operate at lower temperatures than thermosets because only weak Van der Waals forces hold the chains together
- Ceramics can operate at high temperature because covalent bonds are very stable
- Polystyrene has a maximum use temperature below 100oC - which explains why polystyrene coffee cups go out of shape
Example Uses
- Teflon as a non stick surface for frying pans
- Ceramic for fire bricks and for coatings for jet engine blades
- Tungsten for light bulb filaments
Simple Questions
- Why is lead-tin used for solder?
- Select materials for a saucepan.
- Select materials for a mould for casting aluminium parts (melting temp 660oC)
- Select materials for a mould for casting steel parts (melting temp 1540oC)
Further Questions
- Why can polymers operate only at low temperatures when their polymer chains contain covalent bonds like ceramics?
- What is the operating temperature of a light bulb filament?
There are 2 separate populations for this class to improve clarity. Move the mouse over different parts of the class name to reveal each one.
Select chart: